Kathmandu plane crash: Probe blames Saurya Airlines tragedy on cargo shift, speed errors and oversight lapses
Jul 18, 2025
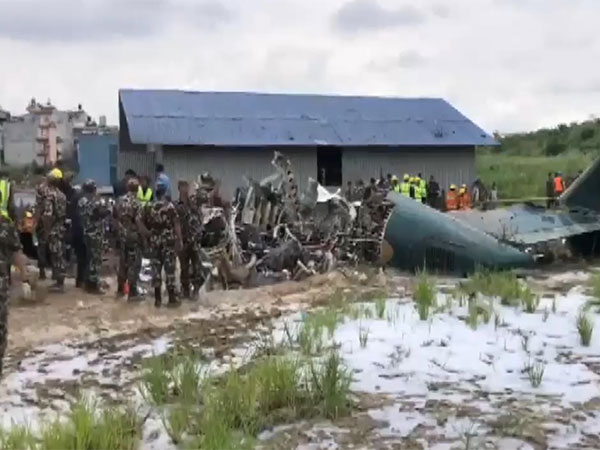
Kathmandu [Nepal], July 18 : An investigation into the July 24, 2024, Saurya Airlines crash in Nepal's Kathmandu has revealed multiple technical and manual lapses as the primary causes of the tragic incident that claimed 18 lives, leaving only the pilot alive.
The Aircraft Accident Investigation Commission (AAIC) released its final report on Friday, citing several critical lapses in weight and balance management, incorrect takeoff speeds, and regulatory oversight failures as key contributing factors to the crash of the Bombardier CRJ-200 aircraft (registration 9N-AME). One of the major findings was that the aircraft's cargo was likely not secured according to guidelines, which may have shifted during takeoff.
The AAIC also pointed out that the takeoff speeds (V-speeds) entered and used by the crew did not match official reference speeds from the aircraft's Quick Reference Handbook (QRH), raising the risk of aerodynamic instability as one of the reasons for the fatal crash.
The Commission also attributed the pitch rate during takeoff, which reached an abnormal 8.6° per second, nearly triple the aircraft's safe limit of 3°/s, as the third reason contributing to the accident. In addition, the commission also flagged the lack of regulatory oversight in approving the ferry flight without verifying compliance with safety protocols.
The Pokhara-bound aircraft, which had been grounded for 34 days prior to the crash and was scheduled for base maintenance in Pokhara, had undergone short-term storage procedures multiple times and had its return-to-service check completed on the morning of the accident.
"While the aircraft had a valid airworthiness certificate, its maintenance records showed time extensions and short-term preparations rather than a long-term, thorough maintenance regime," the report states.
The pilot-in-command had over 6,000 hours of total flight time and nearly 5,000 on the CRJ-200, with valid licenses and recent rest. The first officer was less experienced, with around 1,800 total flight hours.
There was also a supernumerary (S/N) engineer on board. Despite the apparent fitness of the crew and aircraft, crucial oversights in weight documentation, speed settings, and preflight planning may have compromised the safety of the flight.
The ill-fated aircraft, bound for Pokhara, was carrying 19 individuals and 600 kg of baggage. The total takeoff weight was 18,132 kg, and the centre of gravity (CG) was at 20 per cent of the MAC (Mean Aerodynamic Chord) with a stabiliser trim set to 6. The report also has highlighted that the cargo loading protocols are insufficient.
Investigators found that cargo and baggage may not have been properly secured with straps or nets, as required by the airline's own Ground Handling Manual. Shifting loads during takeoff can significantly impact balance and control, especially in a rear-heavy configuration.
"The incorrect stabiliser setting or unbalanced CG may have contributed to the rapid pitch-up, causing a stall or loss of control," the report states.
The AAIC also identified non-compliance with standard loading procedures as a key safety violation, emphasising that such oversights are unacceptable even in ferry or non-revenue flights. Along with the Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal (CAAN), the oversight body of the aviation regulatory body of the Himalayan nation lacks oversight.
Saurya Airlines obtained ferry flight approval for this non-revenue flight from Kathmandu to Pokhara. However, investigators found that the flight permission process was inadequately followed.
"The required documentation, including full compliance with CAAN's 2015 Flight Permission Manual, was incomplete or missing. This regulatory lapse enabled a flight to proceed without proper checks on critical safety elements like load distribution and updated speed charts," it states.
In its report, the AAIC has recommended that CAAN (Civil Aviation Authority) urgently review and revise procedures for ferry and non-scheduled flights to ensure such incidents do not recur.
The Flight Data Recorder (FDR) and Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) were successfully recovered and analysed in Singapore, with oversight from Nepal's AAIC and international observers from Canada, the USA, and the FAA.
"The data showed that the aircraft's engines functioned normally during the event. However, a dangerously high pitch rate, peaking at 8.6° per second, was recorded during rotation, far exceeding safe limits," the AAIC report states.
"The CVR recorded multiple stick shaker activations, indicating stall warnings. The aircraft also exhibited erratic roll movements: right, then left, and again right. Despite the pilot-in-command's attempts to correct the aircraft's attitude using control wheel inputs, the instability continued until impact," it adds further.
Three interim safety recommendations have been issued further by the AAIC, where it has mentioned, "all airline operators in Nepal must immediately review their speed cards and Reduced Takeoff Weight (RTOW) charts to ensure accuracy and conformity with the aircraft manuals."
Also, the strict compliance with cargo and baggage handling procedures is mandated for all the operating airlines, where "every piece of baggage or cargo must be weighed, correctly distributed, and securely fastened using nets or straps."
Along with the regulatory body, the Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal must revise and improve its procedures for granting flight permissions, especially for non-scheduled and ferry flights.
On July 24, 2024, the Saurya Airlines Bombardier CRJ 200 aircraft (registration 9N-AME) crashed shortly after takeoff at Tribhuvan International Airport (TIA) in Kathmandu.
The aircraft was on a ferry flight to Pokhara for scheduled maintenance, carrying 19 airline personnel, including pilots and engineers. Within seconds of liftoff from runway 02 at around 11:11 AM local time, the plane veered sharply right and crashed near runway 20, erupting in flames.
Rescue teams, including firefighters, police, and army personnel, responded swiftly, extinguishing the fire and recovering the bodies, later sent for autopsy. The crash prompted a temporary shutdown of TIA, disrupting domestic and international flights.
The government-formed investigation committee submitted its report following the Saurya Airlines Bombardier CRJ-200 crash that occurred on July 24, 2024. The five-member commission was established immediately after the accident during an emergency Cabinet meeting to determine the causes of the crash.
It was led by Ratish Chandra Lal Suman, the former Director General of the Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal (CAAN). The other members were Captain Dipu Jwarchan, Professors Kuldip Bhattarai and Sanjay Adhikari from Pulchowk Engineering Campus, and Mukesh Dangol, an Air Traffic Control Officer at CAAN.
The committee completed its investigation and submitted the report, providing detailed findings on the circumstances and factors that led to the tragic accident, which claimed 18 lives.